Lab Services
Ergonomics Laboratory Services
- Quantification of Human Performance
- Product Testing & Competitive Product Bench-marking
- Ergonomic Product Certification
- User Experience and Interface Analysis
- Validation of product claims
- Human Productivity Testing
Click here to download a brochure of US Ergonomics’ Product Testing Services
Testing Techniques
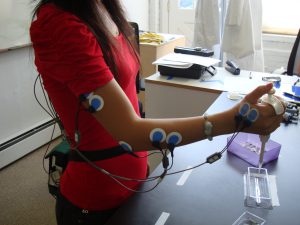
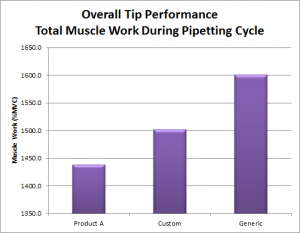
Muscle Exertion: Electromyography (EMG) is a measurement of the muscle effort levels required to perform a job or use a particular tool or type of equipment. Applied to most muscle groups this technique can be used to measure effort and predict fatigue potential. It is often used to compare products or work techniques. Thresholds of exertion may be used to determine if a design is acceptable.
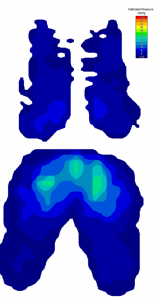
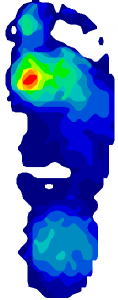
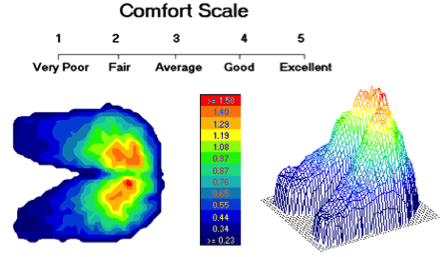
Contact Pressure Mapping: Contact Pressure is measured using flexible force sensors. Typically placed at key contact areas this technique can record the level of pressure between the user and the product interface. Examples of application include assessments of seat pressure distribution, hand tool contact and/or footwear support.
Full Body Motion Capture: Using a state-of-the-art motion capture system, postural patterns and habits can be recorded to build a motion database for a work task. Using that database, training can be developed to optimize productivity while reducing the ergonomic exposure to employees by identifying bad habits, and detecting when they occur.
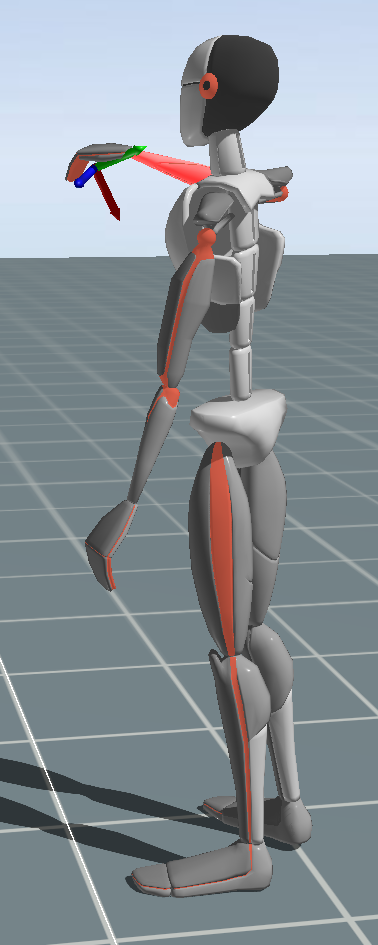

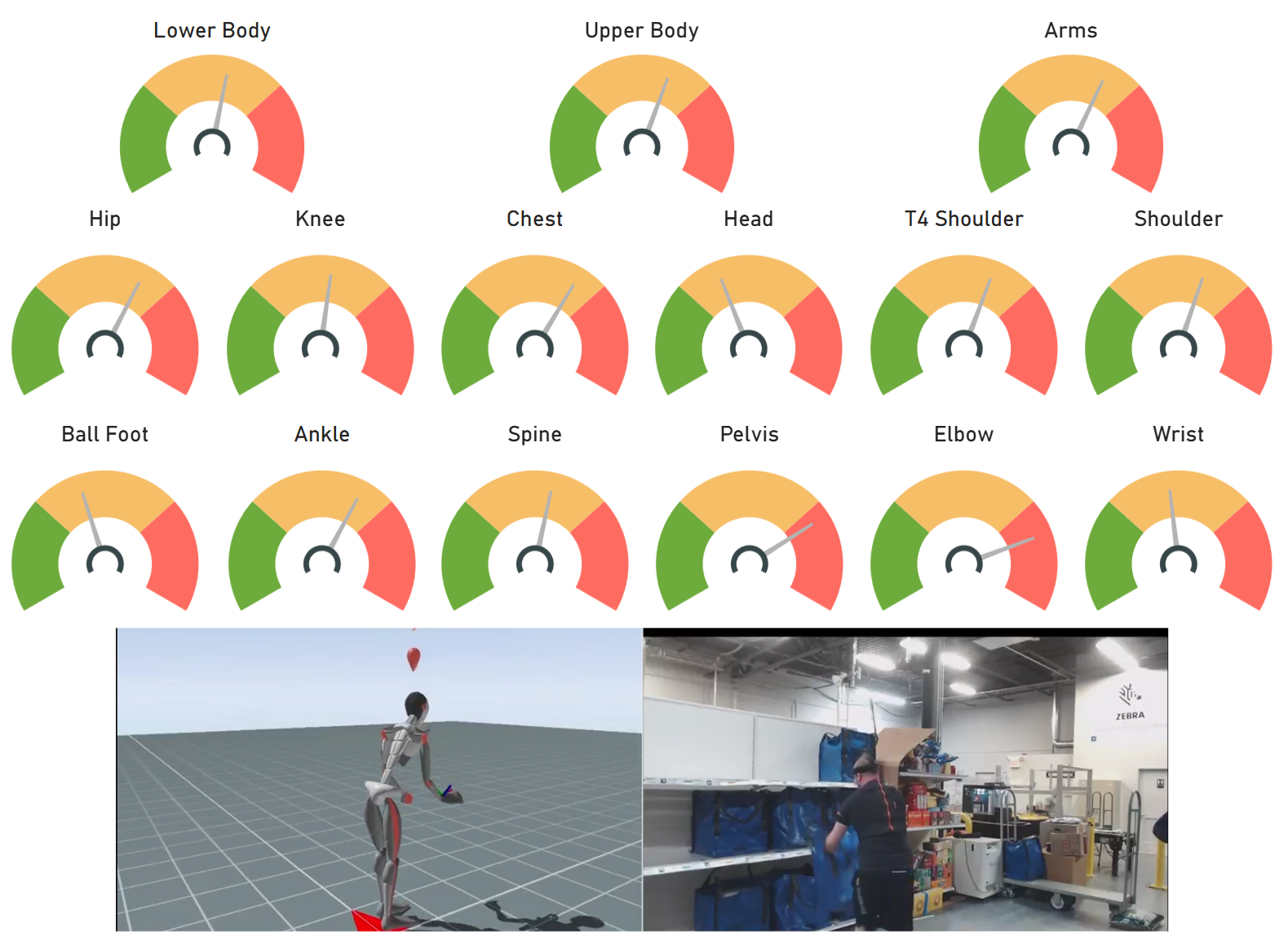
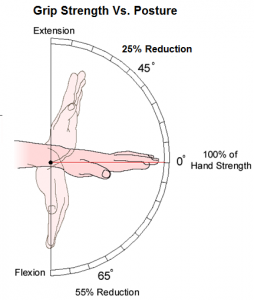
Dynamic Posture: Postural technique is directly related to joint stress and exertion levels. The postures associated with work or product use will directly impact productivity and ergonomic risk. Methods to measure postural technique include electrogoniometry and video based analysis. Three-dimensional kinematic analyses of body movement are used to assess effort and performance levels.
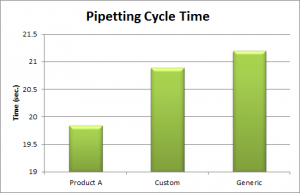
User Productivity: Doing more work with less effort is the definition of ergonomic productivity. Measurable gains in work efficiency are achievable through better technique, better products or better job design. Human efficiency can be dramatically improved while simultaneously reducing ergonomic risks and enhancing employee/user comfort.
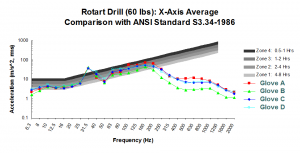
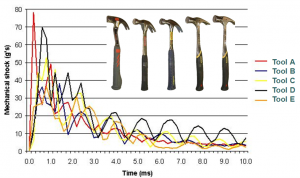
Hand/Arm and Whole Body Human Vibration Testing: Vibration of the whole body, hand, and arm are measured in accordance with published standards (ISO, ANSI, EU). Based on the vibration magnitude and frequency, safe exposure limits may be determined. Hand/arm vibration tests are typically conducted on powered hand tools (assembly tools, grinders, jack hammers, etc.). Whole body vibration tests are typically performed on ride on vehicles (lift trucks, automobiles, etc.) or vibrating floor areas.

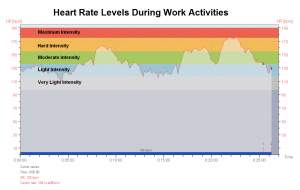
Physiologic Work Load: Heart Rate is measured to assess whole body fatigue potential and to determine appropriate work/rest schedules. The cardiovascular requirements of work should also be considered in the development of pre-employment screening programs.
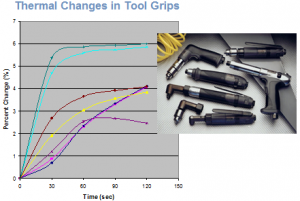
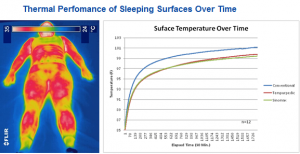
Thermal Performance: Skin sensitivity to moderately warm or cold temperatures can affect comfort, usability and injury potential. To quantify the thermal characteristics of materials that come in contact with the skin, surface temperature may be measured. Common applications include seating, hand tools, mattresses and other product that a user may come in contact with. The thermal performance may allow product comparisons or be assessed relative to desirable thermal limits.
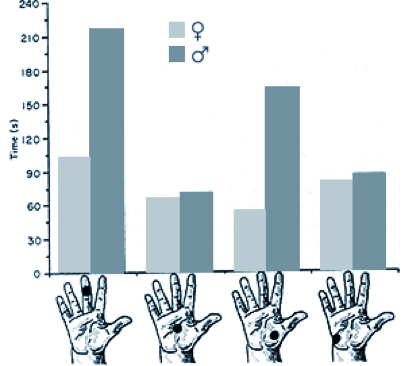
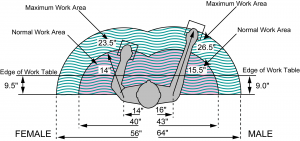
Anthropometric Analyses: Anthropometric analyses considers the variation in human body size & shape, range of joint motion and strength. Anthropometric data may be obtained from various global populations. It is applied to ensure that a design meets the requirements of its intended user’s physical capabilities.
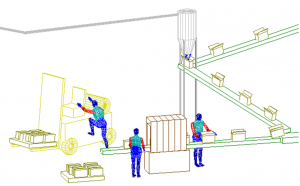
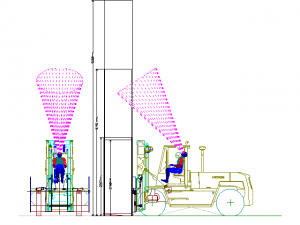
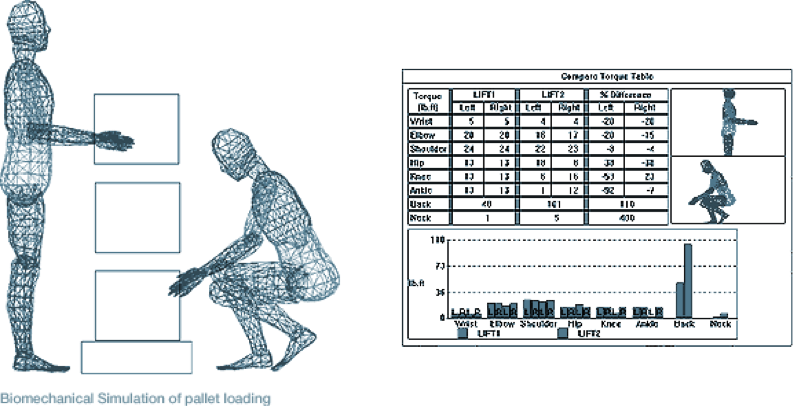
Human CAD Analysis : 3-dimensional evaluation of equipment or processes may be completed using Computer Aided Design tools. A computer generated humanoid may be selected from various percentile groups and/or global populations to simulate activities. The technique allows an objective design comparison related to joint forces and torques, sizing, reach and vision ranges and more.
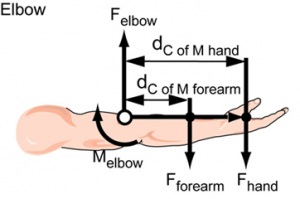
Biomechanical Modeling & Simulation: Biomechanical Modeling is applied to simulate the effects of a product or job design on the human. Calculations of joint forces and torques as well as spinal disc pressures may be compared to population limitations. Modeling also allows design concepts to be evaluated in a virtual state. The NIOSH Lifting Analysis and University of Michigan 3-D Static Strength prediction model are among some of the techniques applied.
Psychometric Testing: a variety of subjective survey methodologies to assess user comfort and preference. These subjective ratings may be correlated to objective measures and variables to develop comfort prediction models. For example, US-Ergo ergonomists have developed several models for predicting seated comfort using measurements of contact pressure.